In today’s digital age, traditional artists face unique challenges in protecting their intellectual property (IP). As art is shared more frequently online, it is essential for artists to understand how copyright and other forms of IP can protect their creative works. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive look at what traditional artists need to know about copyright and intellectual property.
What is Copyright in the Art World?
Copyright is a legal framework that protects original creative works from being used, reproduced, or distributed without permission. For artists, copyright ensures that they have exclusive rights to their artwork, allowing them to control how it is used and who profits from it.
Overview of Copyright Laws for Artists
Copyright automatically applies to an artist’s work as soon as it is created and fixed in a tangible medium, such as a painting, sculpture, or drawing. In most countries, this protection is granted without needing to register the work, though registration can offer additional legal benefits.
Differences Between Copyright and Other IP Protections
While copyright protects the expression of ideas (like a finished painting), other forms of intellectual property—such as trademarks and patents—cover different elements. For example, a trademark protects logos or brand names associated with an artist’s work, while a patent could protect an innovative art tool or process the artist invents.

Types of Intellectual Property Relevant to Artists
Artists may encounter various types of intellectual property, and each serves a specific purpose in safeguarding different aspects of their work.
Copyright vs Trademark vs Patent
- Copyright protects original creative works like paintings, sculptures, or drawings.
- Trademark protects symbols, names, or logos associated with the artist or their brand.
- Patent protects inventions, such as new tools or techniques used in creating art.
How These Protections Work for Traditional Artists
Each of these IP protections offers artists different layers of security. Copyright ensures that no one can legally copy your painting or drawing, while a trademark could protect the logo you use to market your art, and a patent might be applicable if you’ve invented a new artistic tool or process.
Why Copyright is Crucial for Traditional Artists
Copyright is essential because it helps artists safeguard their original works from unauthorized reproduction or use. Without copyright protection, your artwork could be copied, altered, or distributed without your consent, potentially depriving you of both recognition and financial rewards.

Preventing Unlawful Reproduction
By securing copyright for your artwork, you can prevent others from reproducing or distributing your work without your permission. This ensures that you retain control over how and where your art is used.
Protecting Your Unique Style and Technique
Every artist develops a distinctive style, technique, and voice over time. Copyright protection helps ensure that no one can copy your artistic style or methods and present them as their own.
How to Obtain Copyright as a Traditional Artist
Fortunately, artists don’t need to take formal steps to obtain copyright protection. The moment your artwork is completed in a tangible form, copyright protection automatically applies.
Automatic Copyright Protection
In most countries, copyright protection is automatically granted when the work is created. However, you must be able to prove that you are the original creator if any disputes arise.
Registering Copyright for Added Protection
Although copyright is automatically applied, registering your work can offer additional legal benefits. Registered works are easier to protect in legal cases, especially if you need to claim statutory damages in court.
Copyright Infringement and How It Affects Artists
Copyright infringement occurs when someone uses, copies, or distributes your artwork without permission. This can be devastating for artists who rely on their work for income or professional recognition.

Common Examples of Copyright Infringement in Art
- Unauthorized reproductions of your artwork on merchandise or websites
- Plagiarizing an artist’s work and selling it as original
- Creating derivative works without the artist’s consent
Legal Consequences of Copyright Violations
If someone violates your copyright, you can pursue legal action. Penalties for infringement can include fines, compensation for damages, and legal fees. Registered copyright provides an even stronger case in court.
Fair Use Doctrine and Its Implications
Fair use is an exception to copyright law that allows limited use of copyrighted material without permission in certain circumstances, such as commentary, criticism, or education.

What Counts as Fair Use in Art?
Fair use in the art world may include using portions of an artwork for commentary, critique, or education. However, this is a complex area of law, and not all uses qualify as fair use.
How Fair Use Differs from Copyright Infringement
Fair use is distinct from copyright infringement because it allows limited use of copyrighted materials under specific conditions. However, if the use doesn’t meet the legal standards for fair use, it could still be considered infringement.
Licensing Your Artwork
Licensing is a method artists can use to earn income while allowing others to use their work under specific terms.
The Benefits of Licensing Your Art
Licensing your artwork gives others permission to use it in exchange for compensation. This can be a steady source of income while ensuring that you still retain the rights to your work.
Types of Licenses for Artists
- Exclusive License: Grants one party the exclusive right to use the artwork for a set period.
- Non-Exclusive License: Allows multiple parties to use the artwork simultaneously.
- Royalty-Free License: Users pay a one-time fee for indefinite use.
Protecting Your Work on the Internet
With the increase in online sharing, protecting your artwork from digital theft is crucial.
Digital Watermarking and Metadata
One effective way to safeguard your artwork online is by adding digital watermarks or embedding metadata in your images. These techniques help prove ownership and discourage unauthorized use or theft. Watermarking visibly marks your artwork with a logo or text, while metadata is invisible but equally crucial in tracking and protecting your work.
What is Metadata?
Metadata refers to information embedded in a digital file that describes its properties, such as the creator’s name, creation date, copyright details, and usage permissions. It does not alter the visual aspects of the image but provides essential information when someone accesses or uses the file. By embedding metadata in your artwork, you create a digital signature that can serve as proof of ownership and ensure your intellectual property rights are respected.
How to Embed Metadata in Artwork
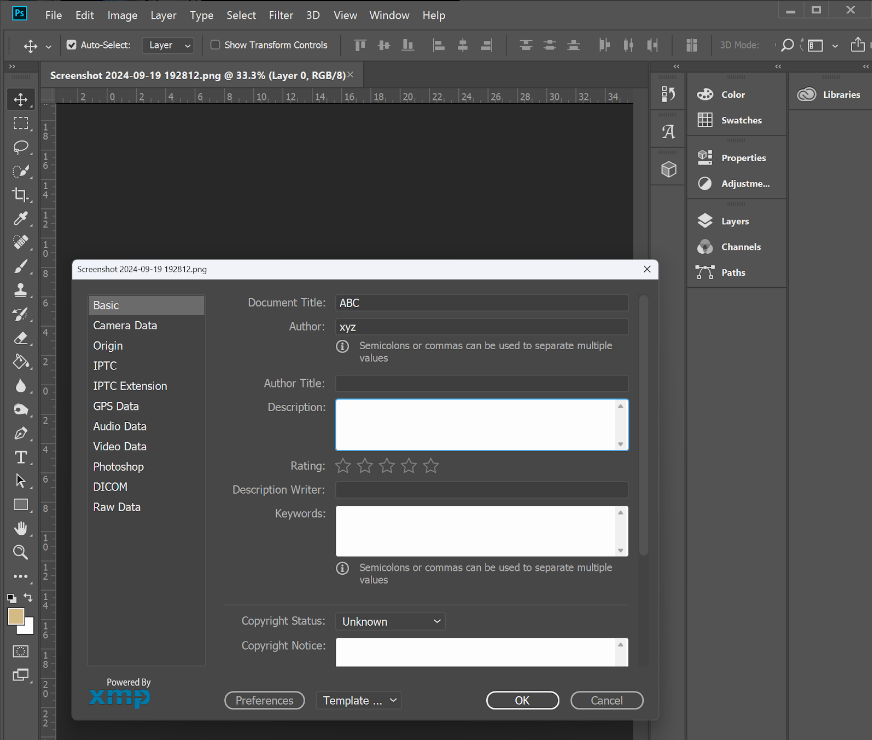
Embedding metadata in your artwork image can be done using various image-editing tools and programs that support metadata entry. Here’s a basic guide on how to embed metadata:
- Using Image Editing Software (e.g., Adobe Photoshop, Lightroom):
- Open your artwork in the software.
- Navigate to the “File” menu and select “File Info” or “Document Info.”
- A metadata panel will appear, allowing you to add details such as:
- Title of the artwork
- Artist’s name
- Copyright information
- Description of the work
Save the changes, and the metadata will be embedded in the image.
2. Using Metadata Tools (e.g., ExifTool, XnView):
These tools allow you to edit and embed metadata specifically. You can manually enter copyright information and other details that will stay with the image file.
3. Online Metadata Embedding:
There are online tools available where you can upload your image and add or edit metadata before downloading the updated file.
By combining digital watermarking with metadata embedding, you ensure a comprehensive approach to protecting your artwork online, making it easier to track and enforce your rights over your creations.
Strategies for Combating Online Copyright Infringement
Artists should regularly monitor where their work is shared and take action against unauthorized use. Tools like reverse image searches can help track down stolen content.

Copyright Protection for International Artists
Artists who sell or display their work internationally need to be aware of how copyright laws differ between countries.
How International Copyright Laws Differ
While many countries follow similar copyright frameworks, the rules aren’t always the same. Some countries may offer stronger or weaker protections, or have different ways of enforcing those protections. It’s important to research the specific copyright laws of any country where you plan to sell or exhibit your work. Understanding these differences can help you avoid legal issues and ensure your artwork is fully protected no matter where it travels.
Navigating Copyright in Cross-Border Transactions
When you’re working internationally, clear communication is key. Make sure your contracts include explicit copyright and licensing terms to avoid misunderstandings. This is especially important when selling your work to collectors abroad or collaborating with international galleries. Properly outlined agreements help protect your rights and ensure both you and your clients are on the same page about how your artwork can be used.

Understanding the Public Domain and Its Role in Art
The public domain consists of creative works no longer protected by copyright, which artists can freely use.
When Art Enters the Public Domain
Art enters the public domain when the copyright expires, which typically happens 70 years after the creator’s death.
Using Public Domain Art in New Creations
Once a work is in the public domain, it can be used by anyone without needing permission. Many artists find inspiration in public domain works, using them as a basis for new creations.

Intellectual Property Management for Traditional Artists
Managing your intellectual property is a key step in ensuring the long-term success of your art career. It helps you stay organized and ensures that your unique creations are always protected.
How to Manage Your Copyright Portfolio
Keeping track of both registered and unregistered works is essential to managing your intellectual property effectively. It might sound like a lot, but organizing your portfolio can make a huge difference in protecting your creations. Consider reaching out to a legal advisor if you need help keeping everything in order—it’s worth the peace of mind!
Using Copyright to Enhance Your Brand
Actively managing your copyrights is a great way to build a strong brand and reputation as an artist. By protecting your unique style and licensing your work, you ensure that you’re in control of how your art is used. This not only boosts your professional image but also safeguards your artistic identity for the future.

Collaborations and Copyright Ownership
When you’re working with other artists, it’s really important to set clear boundaries when it comes to copyright ownership from the very start. Here’s how you can manage it smoothly.
Joint Ownership of Copyright in Collaborative Projects
In most collaborations, copyright is shared between everyone involved. But to avoid any confusion later, it’s always a good idea to have a written agreement. That way, everyone knows exactly what their rights and responsibilities are—making things clearer and more comfortable for everyone.
Managing Copyright Disputes in Collaborations
Sometimes, disagreements can happen over who owns what. If you start with a solid legal agreement, it helps prevent misunderstandings down the road. This ensures that all the creators are fairly recognized and compensated for their contributions.

Copyright Lifespan: How Long Does Protection Last?
Copyright protection usually lasts for the lifetime of the artist and continues for 70 years after their death. Once this period ends, the work enters the public domain, allowing everyone to enjoy and use it freely!
Determining the Duration of Copyright Protection
The length of copyright protection can vary depending on the country, but most follow the “life plus 70 years” standard. It’s a good idea to check your local laws to be sure.
Copyright Renewal and Transfer
In some situations, copyright can be renewed or transferred to others. Many artists include copyright clauses in their wills or contracts to make sure their work is protected even after they pass. It’s a great way to keep your legacy going

Common Myths About Copyright for Traditional Artists
There are quite a few misconceptions about how copyright works, especially when it comes to traditional artists. Let’s clear up a couple of common ones:
Misconceptions About Automatic Copyright
Yes, copyright is automatically granted when you create an original work, but many artists mistakenly think this means they don’t need to take any further steps. Registering your work gives you stronger legal protection and can make it easier to enforce your rights if someone misuses your art.
Misunderstanding Fair Use in Art
Some artists believe they can use copyrighted works freely as long as they aren’t making a profit. But fair use is more complex than that. Not all uses are protected, so it’s important to understand the rules to avoid unintentional infringement.

Steps to Take When Your Copyright is Violated
If you discover that your artwork has been used without your permission, don’t worry—there are steps you can take to protect your rights.
Filing a Copyright Infringement Complaint
You can file a copyright infringement complaint directly with the person who misused your work or take legal action through the courts. Having your copyright registered makes this process smoother and can increase your chances of success.
Seeking Legal Remedies for Copyright Infringement
If someone infringes on your copyright, you can seek legal remedies like monetary compensation or demand that the infringing content be taken down. In more serious cases, the person who violated your rights could face fines or other legal penalties.

Copyright and Art Commissions
When creating commissioned artwork, understanding who owns the copyright is vital.
Understanding Copyright Ownership in Commissioned Works
Unless specified in a contract, the artist typically retains copyright ownership of commissioned works. However, it’s important to clarify this with the client beforehand.
Legal Agreements for Commissioned Art
A clear agreement should outline who owns the copyright, how the art can be used, and any other important terms related to the commissioned work.

Wrapping Up
Protecting your artwork and understanding copyright as a traditional artist is more important than ever in today’s world. By familiarizing yourself with copyright laws, intellectual property rights, and how to safeguard your work, you can ensure your creativity is respected and valued. Whether you’re dealing with commissions, collaborations, or international art transactions, being proactive about your legal rights helps you maintain control over your art and build a sustainable career.
Remember, your art is your unique contribution to the world—by taking steps to protect it, you’re securing both your present and your future as an artist. Don’t hesitate to seek professional advice, keep your work organized, and use the tools available to ensure that your creative journey stays yours.





